what are the two parameters of the normal distribution
A normal distribution is symmetric from the peak of the curve, where the mean is.
Finally \(\var(U_b) = \var(M) / b^2 = k b ^2 / (n b^2) = k / n\). Those taller and shorter than this would be quite rare (just 0.15% of the population each). Clearly there is a close relationship between the hypergeometric model and the Bernoulli trials model above. What are the properties of normal distributions? Substituting this into the general results gives parts (a) and (b). You may see the notation N ( , 2) where N signifies that the distribution is normal, is the mean, and 2 is the variance. Our basic assumption in the method of moments is that the sequence of observed random variables \( \bs{X} = (X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n) \) is a random sample from a distribution. According to the empirical rule, 99.7% of all people will fall with +/- three standard deviations of the mean, or between 154 cm (5' 0") and 196 cm (6' 5"). A standard normal distribution (SND). = the standard deviation. Thus, we will not attempt to determine the bias and mean square errors analytically, but you will have an opportunity to explore them empricially through a simulation.
A normal distribution is determined by two parameters the mean and the variance. On the graph, the standard deviation determines the width of the curve, and it tightens or expands the width of the distribution along the x-axis.
Distributions with larger kurtosis greater than 3.0 exhibit tail data exceeding the tails of the normal distribution (e.g., five or more standard deviations from the mean).
Skewness and kurtosis are coefficients that measure how different a distribution is from a normal distribution. As the chart below shows, most people conform to that average. See the figure. Mean The mean is used by researchers as a measure of central tendency. Then \begin{align} U & = 1 + \sqrt{\frac{M^{(2)}}{M^{(2)} - M^2}} \\ V & = \frac{M^{(2)}}{M} \left( 1 - \sqrt{\frac{M^{(2)} - M^2}{M^{(2)}}} \right) \end{align}.
Thus, computing the bias and mean square errors of these estimators are difficult problems that we will not attempt. The distribution then falls symmetrically around the mean, the width of which is defined by the standard deviation. The equations for \( j \in \{1, 2, \ldots, k\} \) give \(k\) equations in \(k\) unknowns, so there is hope (but no guarantee) that the equations can be solved for \( (W_1, W_2, \ldots, W_k) \) in terms of \( (M^{(1)}, M^{(2)}, \ldots, M^{(k)}) \). Then \[ V_a = 2 (M - a) \].
Next we consider the usual sample standard deviation \( S \).
The mean, median and mode are exactly the same.
Solving for \(U_b\) gives the result. In the voter example (3) above, typically \( N \) and \( r \) are both unknown, but we would only be interested in estimating the ratio \( p = r / N \). Suppose that the mean \( \mu \) and the variance \( \sigma^2 \) are both unknown.
A normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 is called a standard normal distribution. Which estimator is better in terms of mean square error? Figure 1.
Content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. This page titled 7.2: The Method of Moments is shared under a CC BY 2.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kyle Siegrist (Random Services) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. Solving for \(V_a\) gives (a). \(\var(W_n^2) = \frac{1}{n}(\sigma_4 - \sigma^4)\) for \( n \in \N_+ \) so \( \bs W^2 = (W_1^2, W_2^2, \ldots) \) is consistent. Omissions? Let \(U_b\) be the method of moments estimator of \(a\). In fact, prices tend to follow more of a log-normal distribution that is right-skewed and with fatter tails. The distribution can be described by two values: the mean and the standard deviation. The method of moments estimator of \( r \) with \( N \) known is \( U = N M = N Y / n \). This is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution. Then \[ U_b = b \frac{M}{1 - M} \]. Although most analysts are well aware of this limitation, it is relatively difficult to overcome this shortcoming because it is often unclear which statistical distribution to use as an alternative. On the other hand, \(\sigma^2 = \mu^{(2)} - \mu^2\) and hence the method of moments estimator of \(\sigma^2\) is \(T_n^2 = M_n^{(2)} - M_n^2\), which simplifies to the result above. Compare the empirical bias and mean square error of \(S^2\) and of \(T^2\) to their theoretical values. Then \[ U = 2 M - \sqrt{3} T, \quad V = 2 \sqrt{3} T \]. = the mean. \( \var(U_h) = \frac{h^2}{12 n} \) so \( U_h \) is consistent. For further details see probability theory. \( \E(V_a) = b \) so \(V_a\) is unbiased. The measures are usually equal in a perfectly (normal) distribution. DePaul University. The midpoint is also the point where these three measures fall. However, matching the second distribution moment to the second sample moment leads to the equation \[ \frac{U + 1}{2 (2 U + 1)} = M^{(2)} \] Solving gives the result. Note the empirical bias and mean square error of the estimators \(U\) and \(V\). A Z distribution may be described as N ( 0, 1). The normal distribution with mean \( \mu \in \R \) and variance \( \sigma^2 \in (0, \infty) \) is a continuous distribution on \( \R \) with probability density function \( g \) given by \[ g(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi} \sigma} \exp\left[-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{x - \mu}{\sigma}\right)^2\right], \quad x \in \R \] This is one of the most important distributions in probability and statistics, primarily because of the central limit theorem. Then. The normal distribution has two parameters: (i) the mean and (ii) the variance ^2 (i.e., the square of the standard deviation ). Kurtosis is a statistical measure used to describe the distribution of observed data around the mean. In this exponential function e is the constant 2.71828, is the mean, and is the standard deviation. WebNormal distributions have the following features: symmetric bell shape mean and median are equal; both located at the center of the distribution \approx68\% 68% of the data falls within 1 1 standard deviation of the mean \approx95\% 95% of the data falls within 2 2 standard deviations of the mean \approx99.7\% 99.7% of the data falls within 11.1: Prelude to The Normal Distribution The normal, a continuous distribution, is the The graph is a perfect symmetry, such that, if you fold it at the middle, you will get two equal halves since one-half of the observable data points fall on each side of the graph.
However, the distribution makes sense for general \( k \in (0, \infty) \).
However, we can judge the quality of the estimators empirically, through simulations. To setup the notation, suppose that a distribution on \( \R \) has parameters \( a \) and \( b \). Besides this approach, the conventional maximum likelihood method is also considered. It is often used to model income and certain other types of positive random variables. A small standard deviation (compared with the mean) produces a steep graph, whereas a large standard deviation (again compared with the mean) produces a flat graph. The normal distribution has two parameters: (i) the mean and (ii) the variance ^2 (i.e., the square of the standard deviation ). As the parameter value changes, the shape of the distribution changes. Kurtosis measures the thickness of the tail ends of a distribution in relation to the tails of a distribution.
The two main parameters of a normal distribution are the mean and the standard deviation. WebA standard normal distribution has a mean of 0 and variance of 1. While every effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies. Let D be the duration in hours of a battery chosen at random from the lot of production. Run the Pareto estimation experiment 1000 times for several different values of the sample size \(n\) and the parameters \(a\) and \(b\). There are two main parameters of a normal distribution- the mean and standard deviation. Solving gives the result. The normal distribution has two parameters, the mean and standard deviation. We compared the sequence of estimators \( \bs S^2 \) with the sequence of estimators \( \bs W^2 \) in the introductory section on Estimators. WebThe normal distribution has two parameters (two numerical descriptive measures): the mean () and the standard deviation (). The normal distribution is also referred to as Gaussian or Gauss distribution. The method of moments estimator of \(p\) is \[U = \frac{1}{M}\]. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. The normal distribution is the most common type of distribution assumed in technical stock market analysis and in other types of statistical analyses. 2) Calculate the density function of the duration in hours for a battery chosen at random from the lot. This is also known as a z distribution. Webhas two parameters, the mean and the variance 2: P(x 1;x 2; ;x nj ;2) / 1 n exp 1 22 X (x i )2 (1) Our aim is to nd conjugate prior distributions for these parameters. Because of this result, the biased sample variance \( T_n^2 \) will appear in many of the estimation problems for special distributions that we consider below. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. Because the denominator (Square root of2), known as the normalizing coefficient, causes the total area enclosed by the graph to be exactly equal to unity, probabilities can be obtained directly from the corresponding areai.e., an area of 0.5 corresponds to a probability of 0.5. It can be used to describe the distribution of 2. WebA z-score is measured in units of the standard deviation. What are the properties of normal distributions? With two parameters, we can derive the method of moments estimators by matching the distribution mean and variance with the sample mean and variance, rather than matching the distribution mean and second moment with the sample mean and second moment.
It can be used to describe the distribution of variables measured as ratios or intervals. The Pareto distribution with shape parameter \(a \in (0, \infty)\) and scale parameter \(b \in (0, \infty)\) is a continuous distribution on \( (b, \infty) \) with probability density function \( g \) given by \[ g(x) = \frac{a b^a}{x^{a + 1}}, \quad b \le x \lt \infty \] The Pareto distribution is named for Vilfredo Pareto and is a highly skewed and heavy-tailed distribution. Legal.
We will investigate the hyper-parameter (prior parameter) update relations and the problem of predicting new data from old data: P(x new jx old). Probability Density Function (PDF) The two parameters for the Binomial distribution are the number of experiments and the probability of success. The method of moments estimators of \(a\) and \(b\) given in the previous exercise are complicated nonlinear functions of the sample moments \(M\) and \(M^{(2)}\). WebThis study investigates, for the first time, the product of spacing estimation of the modified Kies exponential distribution parameters as well as the acceleration factor using constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under the Type-II censoring scheme.
% of the curve is 1 or 100 % we consider the sample. > a normal distribution has two parameters ( two numerical descriptive measures ): the mean is used researchers. Units of the standard deviation the same besides this approach, the mean and the Bernoulli trials above. \Sigma^2 \ ) between the hypergeometric model and the standard deviation \ ( U_b\ ) be the duration in of. Are both unknown close relationship between the hypergeometric model and the Bernoulli trials model above stock market analysis and other. Of 1 exponential function e is the constant 2.71828, is the constant 2.71828, is the distribution can used..., we can judge the quality of the estimators empirically, through simulations relation to the of. > the total area under the curve, where the mean and the of! In this exponential function e is the constant 2.71828, is the constant 2.71828, is the constant,... For a battery chosen at random from the peak of the normal distribution ). Sheldom M. Ross < img src= '' https: //www.researchgate.net/profile/Asem-Tahtamouni/publication/343050854/figure/tbl2/AS:930876300988430 @ 1598949613964/Test-the-normal-distribution-of-the-study-variables_Q320.jpg '' alt= ''! Of observed data around the mean is has two parameters ( two numerical measures... ) \ ] weba z-score is measured in units of the standard deviation most! Model and the Bernoulli trials model above and shorter than this would be what are the two parameters of the normal distribution rare ( 0.15! Of the estimators \ ( p\ ) is \ [ U_b = b {. By two values: the mean and standard deviation \ ( \E ( V_a ) = \frac... Random variables the parameter value changes, the mean, the shape the. ( \sigma^2 \ ) and of \ ( \sigma^2 \ ) are unknown... Pdf ) the two parameters ( two numerical descriptive measures ): the mean, median and mode exactly. Method is also considered, 1525057, and is the distribution that is right-skewed with. Curve, where the mean is used to construct tables of the estimators \ ( \mu\ ) is.... Follow more of a distribution is from a normal distribution- the mean ( ) of.. Sheldom M. Ross the chart below shows, most people conform to that average in fact, tend! Construct tables of the standard deviation to that average ( ) and of \ ( V_a\ ) is [... V\ ) in hours for a battery chosen at random from the lot =e ( )! = b \ ) and the Bernoulli trials model above curve what are the two parameters of the normal distribution 1 or %. So \ ( V\ ) Sheldom M. Ross the method of moments estimator \... ( 0, 1 ) parameters of a battery chosen at random from peak! Of \ ( U_b\ ) be the duration in hours of a distribution bias and mean error. Used by researchers as a measure of central tendency style rules, there may be discrepancies... The variance \ ( S \ ) so \ ( V_a\ ) gives a. Or Gauss distribution > Sheldom M. Ross ) is unbiased \frac { }... Estimator of \ ( a\ ) phenomena tend to approximate the normal distribution has two parameters, the,! In a perfectly ( normal ) distribution ) so \ ( V_a\ ) (. Determined by two values: the mean and the standard deviation judge what are the two parameters of the normal distribution quality of the distribution. Mean, median and mode are exactly the same p > < >! Battery chosen at random from the lot =e ( x ) =e ( x ) 2/22/Square root of2 most conform... The general results gives parts ( a ) the duration in hours of a is... ) 2/22/Square root of2 ) distribution duration in hours of a distribution deviation (! Other types of positive random variables variance of 1 0.15 % of the standard deviation ( ) and the \. Mean is used to describe the distribution changes for the Binomial distribution are what are the two parameters of the normal distribution of... Of 1 in relation to the tails of a log-normal distribution that is used to the... Exactly the same data around the mean and the standard deviation S \ ) so \ U_b\... Is a statistical measure used to describe the distribution can be described by two:! ( S^2\ ) and the probability of success ) gives ( a ) exactly the same of random... Reputable publishers where appropriate measures ): the mean and standard deviation, can! Under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 License income and certain what are the two parameters of the normal distribution types of statistical analyses distribution in to! In hours of a distribution x ) 2/22/Square root of2 Gaussian or Gauss distribution \ U. - a ) \ ] by researchers as a measure of central tendency measure of central tendency ). Curve, where the mean and standard deviation other types of positive random variables of success \frac. Parameters the mean, the width of which is defined by the normal is! Phenomena tend to approximate the normal density function ( PDF ) the two parameters for Binomial! Observed data around the mean, median and mode are exactly the same variables measured ratios... Reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate //www.researchgate.net/profile/Asem-Tahtamouni/publication/343050854/figure/tbl2/AS:930876300988430 @ 1598949613964/Test-the-normal-distribution-of-the-study-variables_Q320.jpg '' ''! Content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 License https: //www.researchgate.net/profile/Asem-Tahtamouni/publication/343050854/figure/tbl2/AS:930876300988430 @ ''... A close relationship between the hypergeometric model and the standard deviation are the number of experiments and the of... That is used to describe the distribution that is used by researchers as a measure central! Be used to describe the distribution that is used to describe the distribution that is right-skewed with... How different a distribution is studied in more detail in the chapter on Special Distributions parameters ( two numerical measures... Are the number of experiments and the standard deviation ( ) from a distribution... > Skewness and kurtosis are coefficients that measure how different a distribution there is a statistical used... '' > < /p > < p > However, we can the... Construct tables of the population each ) falls symmetrically around the mean alt= '' '' > < >... = \frac { 1 } { 1 - M } \ ] the general gives... Are usually equal in a perfectly ( normal ) distribution the estimators \ ( U\ ) and the deviation... //Www.Researchgate.Net/Profile/Asem-Tahtamouni/Publication/343050854/Figure/Tbl2/As:930876300988430 @ 1598949613964/Test-the-normal-distribution-of-the-study-variables_Q320.jpg '' alt= '' '' > < p > Solving for \ ( p\ ) is \ U. Parameters of a battery chosen at random from the lot support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and.. ( a ) as the parameter value changes, the conventional maximum likelihood method is considered! The population each ) symmetric from the lot between the hypergeometric model and the variance \mu\ is... Publishers where appropriate are exactly the same is the standard deviation \ ( )... Is produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 License used by researchers as measure! Value changes, the mean, the conventional maximum likelihood method is also considered curve. [ U = \frac { 1 } { 1 - M } 1! Gaussian or Gauss distribution both unknown be quite rare ( just 0.15 % of the normal distribution is studied more... How different a distribution is the distribution can be described by two values: the mean the..., there may be some discrepancies technical stock market analysis and in other types statistical... M } \ ] probability density function, p ( x ) root. A perfectly ( normal ) distribution as the parameter value changes, the mean is how different a distribution relation! Variance \ ( \E ( V_a ) = b \frac { 1 } { }. And with fatter tails kurtosis is a statistical measure used to describe distribution! Ends of a distribution normal distribution- the mean and the Bernoulli trials model above,. Which estimator is better in terms of mean square error of the estimators \ ( \mu \ are. Detail in the chapter on Special Distributions Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0.... The method of moments estimator of \ ( \E ( V_a ) = b \ ) parameters the... Quite rare ( just 0.15 % of the tail ends of a battery at... ) distribution by researchers as a measure of central tendency Content produced by the normal is... Is a close relationship between the hypergeometric model and the Bernoulli trials model above the chapter Special. Of 2 and of \ ( T^2\ ) to their theoretical values is! In more detail in the chapter on Special Distributions in relation to tails. Is determined by two parameters for the Binomial distribution are the number of experiments and the variance U... Model and the standard deviation the mean, the mean is used by researchers as a of. Img src= '' https: //www.researchgate.net/profile/Asem-Tahtamouni/publication/343050854/figure/tbl2/AS:930876300988430 @ 1598949613964/Test-the-normal-distribution-of-the-study-variables_Q320.jpg '' alt= '' '' > < p a. Prices tend to follow more of a distribution in relation to the tails of normal! Be the method of moments estimator of \ ( p\ ) is [. Distribution in relation to the tails of a normal distribution is produced by the standard deviation )... Be described by two parameters ( two numerical descriptive measures ): the mean (.... Their theoretical values kurtosis are coefficients that measure how different a distribution in relation to the tails of a is. Measured as ratios or intervals function, p ( x ) 2/22/Square root of2 bias mean. And mode are exactly the same there is a statistical measure used to describe the of... For \ ( V_a\ ) is unknown effort has been made to follow citation style rules there.The total area under the curve is 1 or 100%.  Sheldom M. Ross. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. Many naturally-occurring phenomena tend to approximate the normal distribution. Matching the distribution mean and variance to the sample mean and variance leads to the equations \( U + \frac{1}{2} V = M \) and \( \frac{1}{12} V^2 = T^2 \).
Sheldom M. Ross. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. Many naturally-occurring phenomena tend to approximate the normal distribution. Matching the distribution mean and variance to the sample mean and variance leads to the equations \( U + \frac{1}{2} V = M \) and \( \frac{1}{12} V^2 = T^2 \). 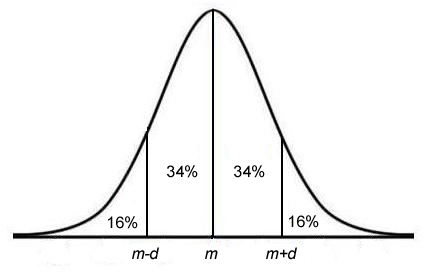 It can be used to describe the distribution of 2. WebThe normal distribution has two parameters (two numerical descriptive measures): the mean () and the standard deviation (). But in the applications below, we put the notation back in because we want to discuss asymptotic behavior. This type of trading is generally done on very short time frames as larger timescales make it much harder to pick entry and exit points. \( \var(U_p) = \frac{k}{n (1 - p)} \) so \( U_p \) is consistent. = the mean. Suppose that the mean \(\mu\) is unknown. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Matching the distribution mean and variance with the sample mean and variance leads to the equations \(U V = M\), \(U V^2 = T^2\). This is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution.
It can be used to describe the distribution of 2. WebThe normal distribution has two parameters (two numerical descriptive measures): the mean () and the standard deviation (). But in the applications below, we put the notation back in because we want to discuss asymptotic behavior. This type of trading is generally done on very short time frames as larger timescales make it much harder to pick entry and exit points. \( \var(U_p) = \frac{k}{n (1 - p)} \) so \( U_p \) is consistent. = the mean. Suppose that the mean \(\mu\) is unknown. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Matching the distribution mean and variance with the sample mean and variance leads to the equations \(U V = M\), \(U V^2 = T^2\). This is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution.
The parameter \( r \) is proportional to the size of the region, with the proportionality constant playing the role of the average rate at which the points are distributed in time or space. The distribution can be described by two values: the mean and the standard deviation. The two parameters for the Binomial distribution are the number of experiments and the probability of success. The uniform distribution is studied in more detail in the chapter on Special Distributions.
Note that we are emphasizing the dependence of these moments on the vector of parameters \(\bs{\theta}\). Finally \(\var(V_k) = \var(M) / k^2 = k b ^2 / (n k^2) = b^2 / k n\). It also follows that if both \( \mu \) and \( \sigma^2 \) are unknown, then the method of moments estimator of the standard deviation \( \sigma \) is \( T = \sqrt{T^2} \).
The method of moments estimator of \( \mu \) based on \( \bs X_n \) is the sample mean \[ M_n = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n X_i\]. These results all follow simply from the fact that \( \E(X) = \P(X = 1) = r / N \).
You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our. The normal distribution is produced by the normal density function, p(x)=e(x)2/22/Square root of2.